Periodontitis: Diagnosis and Treatment
Understanding Periodontitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Comprehensive Treatment Approaches
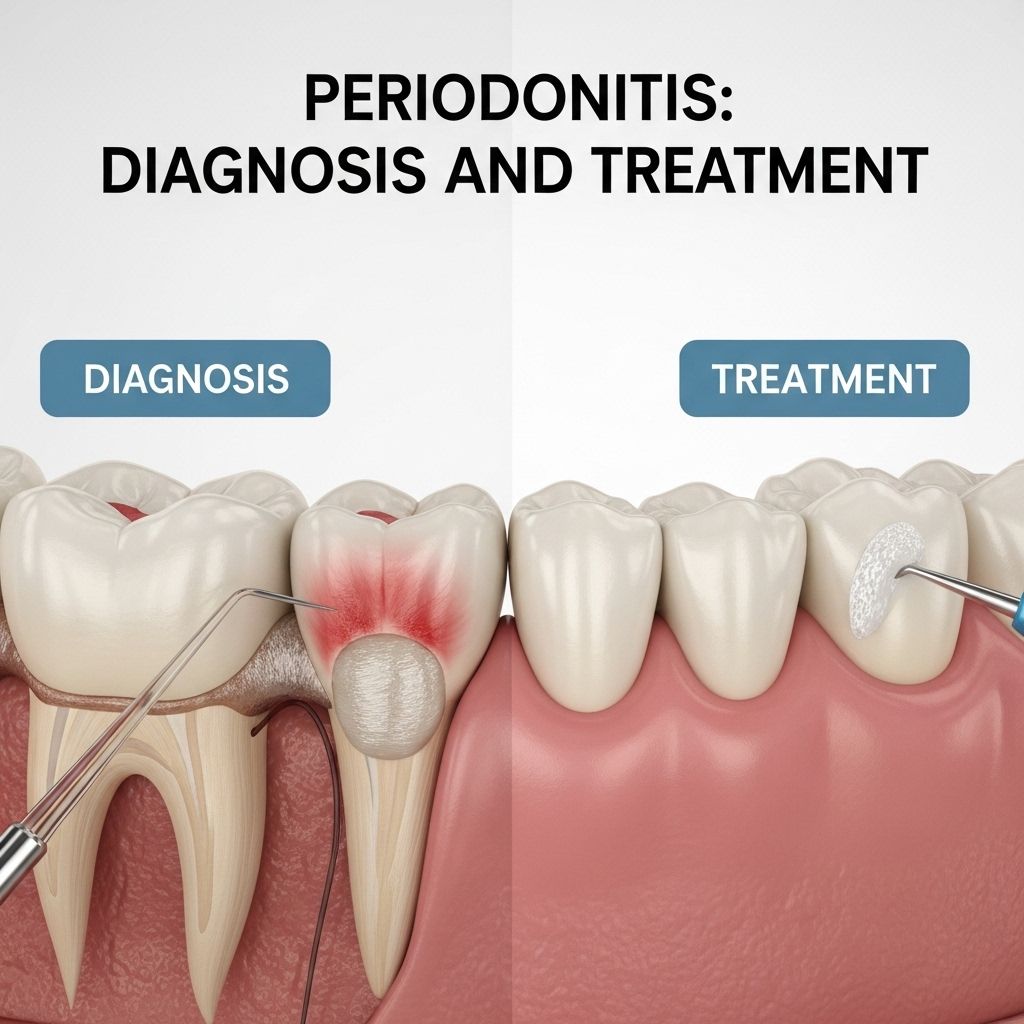
Introduction to Periodontitis
Periodontitis, often referred to as periodontal disease, is a serious infection of the gums that can lead to tooth loss and other health complications if not treated properly. It results from the buildup of plaque and bacteria in the mouth, leading to inflammation and infection of the tissues supporting the teeth. Managing periodontitis requires a comprehensive approach that includes professional dental care and good oral hygiene practices.
Diagnosis of Periodontitis
To diagnose periodontitis, dentists typically follow a series of steps that help assess the severity of the disease:
- Medical History Review: Your dentist will review your medical history to identify factors that might contribute to your symptoms, such as smoking or medications causing dry mouth.
- Mouth Examination: The dentist will examine your mouth for signs of plaque and tartar buildup and check for easy bleeding.
- Pocket Measurement: Using a dental probe, the dentist measures the depth of the pockets between your gums and teeth. Healthy pockets are typically less than 3 millimeters deep, while deeper pockets may indicate periodontitis.
- Dental X-rays: X-rays are taken to check for bone loss around the teeth, which often occurs in advanced stages of periodontitis.
Treatment of Periodontitis
The treatment of periodontitis depends on the severity of the disease. Both surgical and nonsurgical methods are available:
Nonsurgical Treatments
For mild to moderate cases, treatment may involve nonsurgical procedures:
- Scaling: This process removes tartar and bacteria from the surfaces of your teeth and below the gumline. It can be performed using instruments, a laser, or an ultrasonic device.
- Root Planing: This involves smoothing the surfaces of the roots to prevent further buildup of tartar and bacteria, helping your gums reattach to your teeth.
- Antibiotics: Topical or oral antibiotics may be prescribed to control bacterial infections. Topical antibiotics can include mouth rinses or gels placed in the gum pockets.
Surgical Treatments
For advanced periodontitis, surgical treatments may be necessary:
- Flap Surgery (Pocket Reduction Surgery): This involves making incisions in the gums to expose the roots for effective cleaning. The underlying bone may be reshaped before the gum tissue is stitched back.
- Soft Tissue Grafts: These grafts help reinforce damaged gum tissue, reducing further gum loss and improving the appearance of your teeth.
- Bone Grafting: This procedure involves placing a graft made from your own bone, artificial material, or a donor source to support tooth roots and promote bone regrowth.
- Guided Tissue Regeneration: This approach involves placing a barrier to prevent unwanted tissue from growing in the area, allowing bone to regrow naturally.
- Tissue-Stimulating Proteins: These proteins stimulate the growth of healthy bone and tissue around the teeth.
Managing Periodontitis Effectively
Regular dental check-ups and maintaining good oral hygiene are crucial for managing periodontitis effectively. A daily routine of brushing and flossing can help prevent plaque buildup and reduce the risk of infection.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What causes periodontitis?
A: Periodontitis is caused by the buildup of plaque and bacteria in the mouth, leading to infection and inflammation of the gums.
Q: Can periodontitis be cured?
A: While periodontitis cannot be cured, it can be managed effectively through appropriate treatment and good oral hygiene practices.
Q: What are the symptoms of periodontitis?
A: Common symptoms include bleeding gums, bad breath, loose teeth, and a receding gumline.
Q: How is periodontitis diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a review of medical history, mouth examination, pocket measurement, and dental X-rays.
Q: What treatments are available for periodontitis?
A: Treatments include nonsurgical options like scaling and root planing, and surgical procedures such as flap surgery and bone grafting.
Conclusion
Periodontitis is a serious condition that requires prompt and effective management to prevent further complications. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their oral health and overall well-being.
Read full bio of Sneha Tete