Statin Side Effects: Understanding Risks, Benefits, and Management
Comprehensive guide to statin side effects, benefits, and safe usage for cholesterol management and cardiovascular health.

Statins and Their Side Effects: What You Need to Know
Statins are a class of medications widely used for lowering blood cholesterol and reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease. While generally safe and effective for most people, statins can cause a range of side effects — from mild and temporary discomforts to rare but serious complications. Knowing what to expect and how to respond is vital for anyone taking or considering statin therapy.
What Are Statins?
Statins are prescription drugs that inhibit an enzyme in the liver involved in cholesterol production. By reducing LDL (“bad”) cholesterol in the blood, they help lower the risk of heart attack, stroke, and other vascular diseases. Common statin medications include:
- Atorvastatin (Lipitor)
- Simvastatin (Zocor)
- Rosuvastatin (Crestor)
- Pravastatin (Pravachol)
- Lovastatin (Mevacor)
Common Side Effects of Statins
Most people tolerate statins well, but some experience mild side effects soon after starting therapy. The most frequent complaints are:
- Headache
- Nausea or vomiting
- Muscle aches, tenderness, or weakness (myalgia)
- Belly discomfort: cramping, pain, bloating, gas
- Diarrhea or constipation
- Flushing of the skin
- Dizziness
- Drowsiness
- Rash
- Low levels of blood platelets
- Difficulty sleeping
These symptoms are often temporary and may subside as the body adapts to the medication. Report any troubling symptoms to your healthcare provider, who may adjust your dose or recommend a different statin.
Less Common and Potentially Serious Statin Side Effects
While rare, statins can cause more significant health concerns. It’s important to recognize these side effects and act promptly:
- Muscle injury or inflammation (myositis): Statins may occasionally cause muscle cells to break down, leading to pain and muscle weakness. The risk increases with higher statin doses or when combined with certain medications, such as fibrates.
- Rhabdomyolysis: This is a rare but life-threatening condition characterized by severe muscle damage. Symptoms include intense pain throughout the body, profound weakness, and dark (cola-colored) urine. Immediate medical attention is needed if these symptoms occur. The risk is about 1.5 per 100,000 people taking statins.
- Liver damage: Occasional increases in liver enzymes may occur. If mild, medication may continue; high doses rarely cause severe problems. Liver function is typically monitored during treatment.
Muscle Pain and Weakness: What to Look For
Muscle-related symptoms can vary widely in intensity:
- Mild muscle aches: Most common, can affect any muscle group
- Severe muscle pain with weakness: May signal myositis or, rarely, rhabdomyolysis
- Fatigue and difficulty with movement: In rare cases, people report trouble getting out of chairs or walking upstairs
Report sudden or unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness — especially if accompanied by fever, dark urine, or general malaise. Blood tests for enzymes such as creatine kinase can help diagnose muscle injury.
Statins and Diabetes Risk
Statins may mildly increase blood sugar levels, leading to a slight uptick in type 2 diabetes diagnoses, especially among individuals already predisposed. However, for people with diabetes, statins yield significant reductions in heart attack risk, often outweighing this potential downside.
Memory, Confusion, and Cognitive Symptoms
Some people using statins report issues such as memory loss or mental confusion. However, large-scale research has not confirmed a definite link, and some studies suggest that statins may even protect against cognitive decline. If noticeable symptoms arise, consult a healthcare professional about alternatives or potential adjustments.
Liver Concerns
Statins can impact liver function, but severe damage is rare. Mild elevations in liver enzymes may occur after therapy initiation. The following should be considered:
- Routine liver function tests are usually recommended
- Persistent or dramatic increases warrant re-evaluation of the medication
- Symptoms of jaundice, dark urine, or abdominal pain should be reported promptly
Rare Statin Side Effects and Drug Interactions
Beyond muscle and liver-related effects, statins have been linked to:
- Numbness, tingling, or pins-and-needles sensation
- Hair loss
- Rash or skin problems
- Sexual dysfunction (low libido, erectile dysfunction)
- Low platelet levels (rare)
- Pancreatitis, a rare but serious condition causing severe stomach pain
Interactions with other drugs can increase risks; for instance, combining statins with medications like cyclosporine or gemfibrozil may heighten muscle injury risk. Always inform your provider about all medications and supplements you take.
Statins in Special Populations
- Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Statins are not recommended, as studies suggest a risk for birth defects.
- Elderly: Older adults may be more susceptible to side effects and often need lower doses.
Managing and Minimizing Side Effects
If you experience side effects, several strategies can help:
- Speak with your healthcare professional about changing the medication, adjusting doses, or switching to a different statin.
- Never discontinue statins abruptly — always discuss with your provider first.
- Consider lifestyle modifications (diet, exercise) to further lower cholesterol.
- Document symptoms and their timing for accurate assessment.
Coenzyme Q10 and Statins
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a natural enzyme sometimes taken as a supplement by people using statins. Some believe it helps reduce muscle aches, though current research is unclear. If considering CoQ10, discuss with your provider for appropriate dosage and drug interaction assessment.
When to Seek Medical Help
If you experience any of the following, seek prompt medical attention:
- Unexplained severe muscle pain, soreness, or weakness, particularly if accompanied by dark urine
- Symptoms of liver dysfunction, such as yellowing of the skin or eyes, unusual fatigue, or abdominal pain
- Signs of allergic reaction (swelling, rash, trouble breathing)
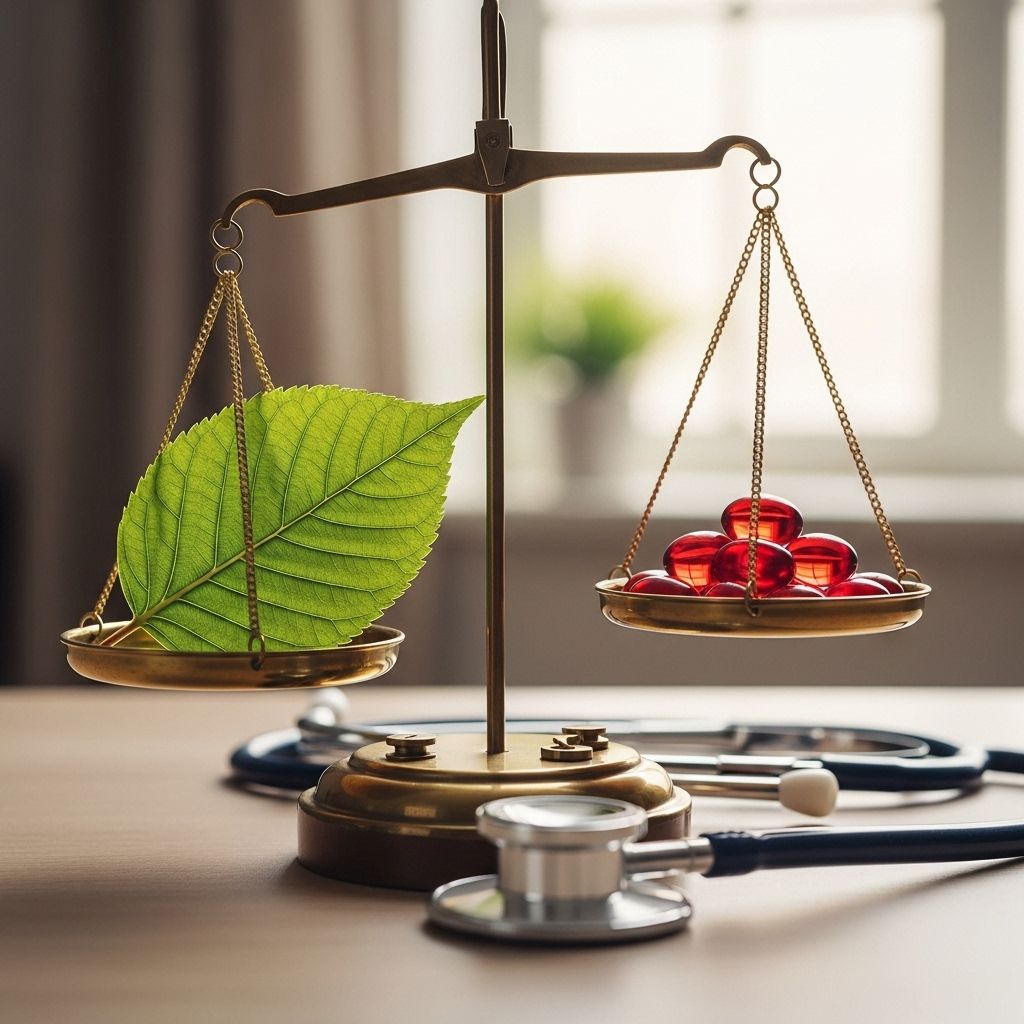
Benefits of Statins vs. Risks
While statins can cause side effects, their proven benefits in lowering heart attack and stroke risk for high-risk individuals usually outweigh the potential harms. Many side effects are manageable or reversible by changing medications or adjusting dosage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: What is rhabdomyolysis, and how do I know if I have it?
A: Rhabdomyolysis is a rare but very serious condition caused by muscle breakdown. Symptoms include severe muscle pain throughout the body, muscle weakness, and cola-colored urine. Seek immediate medical attention if these occur.
Q2: Can statins cause memory loss or confusion?
A: Some people report mental confusion or memory issues with statins, but large studies have not confirmed consistent evidence of this side effect. In some cases, statins may even offer protective cognitive benefits.
Q3: Do statins raise the risk of diabetes?
A: Statins can slightly increase blood sugar levels, especially in those predisposed to diabetes. The cardiovascular benefits often outweigh the minimal risk, especially for people already at high risk of heart disease.
Q4: What should I do if I experience muscle aches or weakness?
A: Mild muscle aches are common but report persistent or severe pain, weakness, or fever to your doctor, as these may indicate serious muscle injury. Diagnostic enzyme tests can help differentiate mild discomfort from more significant problems.
Q5: Should I stop taking statins if I have side effects?
A: Never stop statins without consulting your healthcare provider. Mild side effects can usually be managed by changing the dose or switching the medication. Only stop statins in cases of severe adverse effects and under medical supervision.
Q6: Can statins cause weight gain?
A: Some people may gain weight while using statins, possibly because of increased comfort with diet choices. However, direct causation by the drug itself is not well established.
Tips for Safe Statin Use
- Always discuss any new symptoms with your healthcare professional.
- Inform your doctor about all medications, supplements, and herbal remedies you use.
- Attend regular follow-up visits for cholesterol and liver function tests.
- Practice heart-healthy lifestyle habits alongside medication.
Conclusion: Making Statin Therapy Work For You
Statins remain a cornerstone in heart disease prevention and cholesterol management. Despite potential side effects, most people never experience serious problems. If you are concerned about statin safety, work closely with your provider to develop an individualized approach that balances risk and reward for your long-term health.
Read full bio of Sneha Tete