UTI Diagnosis and Treatment
Understanding Urinary Tract Infections and How to Manage Them
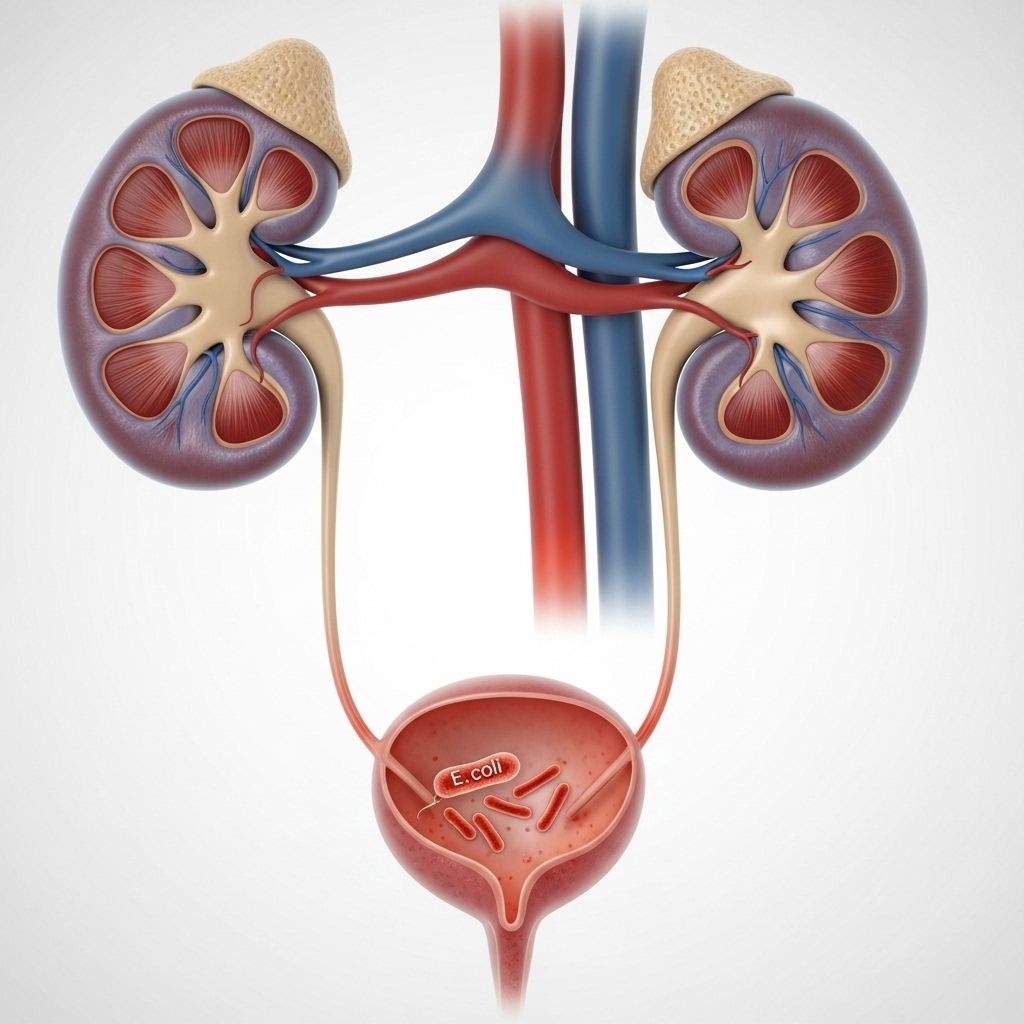
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are bacterial infections that occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, bladder, and urethra. These infections are common, affecting millions of people each year, with women being more susceptible due to their anatomy.
##
Understanding UTIs
UTIs can cause significant discomfort, including a frequent urge to urinate, a burning sensation while urinating, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine. The severity of UTIs can vary, ranging from mild irritations to severe infections that require immediate medical attention.
Symptoms of UTIs
- Frequent or intense need to urinate- Pain or burning sensation while urinating- Cloudy, dark, or bloody urine- Foul-smelling urine- Fever, if the infection has spread to the kidneys- Abdominal pain or pressure in the lower abdomen- Mild to severe nausea or vomiting##Diagnosis of UTIs
Diagnosing a UTI typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history, and lab tests. The most common diagnostic methods include:
–
Urine Sample Analysis
: A healthcare provider may request a urine sample to check for signs of infection, such as white blood cells, red blood cells, or bacteria. It is crucial to collect the sample midstream to avoid contamination.-Urine Culture
: A lab test that identifies the type of bacteria causing the infection, which helps determine the appropriate antibiotic treatment.-Imaging Tests
: For recurrent UTIs, imaging tests like ultrasound, CT scans, or MRI may be used to examine the urinary tract structures for potential abnormalities.-Cystoscopy
: In some cases, a cystoscopy might be performed to visually inspect the inside of the bladder and urethra using a cystoscope.##Treatment of UTIs
Antibiotics are the primary treatment for bacterial UTIs. The choice of antibiotic and the duration of treatment depend on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria involved.
Antibiotics for Simple UTIs
- Trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole (Bactrim, Bactrim DS)- Fosfomycin- Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin, Macrobid, Furadantin)- Cephalexin- CeftriaxoneFor simple UTIs, antibiotics are usually prescribed for a short course, typically lasting 1 to 3 days. However, more severe infections may require longer treatment periods.
Antibiotics for Complicated UTIs
Complicated UTIs, such as those involving the kidneys, may require more potent antibiotics like fluoroquinolones (e.g., ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) and longer treatment durations, often up to several weeks.
For severe infections, hospitalization may be necessary, especially if the infection causes significant symptoms or if there are underlying health issues.
##
Prevention and Management of Recurrent UTIs
Some strategies to prevent recurrent UTIs include:
–
Hydration
: Drinking plenty of water helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract.-Cranberry Products
: Some studies suggest that cranberry juice or supplements may help prevent UTIs by preventing bacteria from adhering to the bladder walls.-Urinating after Sex
: This can help flush out bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity.-Probiotics
: Certain probiotics may support urinary health.-Self-Directed Antibiotic Therapy
: For some individuals with recurrent infections, taking antibiotics at the first sign of symptoms can be effective.## **Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)**Q: Are UTIs contagious?
A: UTIs are not contagious; they are bacterial infections that occur within an individual’s urinary system.
Q: What are the symptoms of a kidney infection?
A: Symptoms include fever, back pain, frequent urination, nausea, and vomiting. If you suspect a kidney infection, seek medical attention immediately.
Q: Can UTIs be treated without antibiotics?
A: Most UTIs are bacterial and require antibiotic treatment. However, some non-bacterial types, like interstitial cystitis, may not involve antibiotics.
Q: How can I prevent UTIs?
A: Prevention strategies include staying hydrated, urinating after sex, avoiding certain foods, and using cranberry products.
Q: What happens if a UTI is left untreated?
A: Untreated UTIs can spread to the kidneys, leading to more severe infections and potentially serious complications if left untreated.
Read full bio of Sneha Tete